Distributed Stream Processing Systems are typically deployed within a single data center in order to achieve high
performance and low-latency computation. The data streams analyzed by such systems are expected to be available in the
same data center. Either the data streams are generated within the data center (e.g., logs, transactions, user clicks)
or they are aggregated by external systems from various sources and buffered into the data center for processing
(e.g., IoT, sensor data, traffic information).
The data center approach for stream processing analytics fits the requirements of the majority of the applications that
exists today. However, for latency sensitive applications, such as real-time decision-making, which relies on analyzing
geographically distributed data streams, a data center approach might not be sufficient. Aggregating data streams incurs
high overheads in terms of latency and bandwidth consumption in addition to the overhead of sending the analysis
outcomes back to where an action needs to be taken.
We propose a new stream processing architecture for efficiently analyzing geographically distributed data streams. Our
approach utilizes emerging distributed virtualized environments, such as Mobile Edge Clouds, to extend stream processing
systems outside the data center in order to push critical parts of the analysis closer to the data sources. This will
enable real-time applications to respond faster to geographically distributed events.
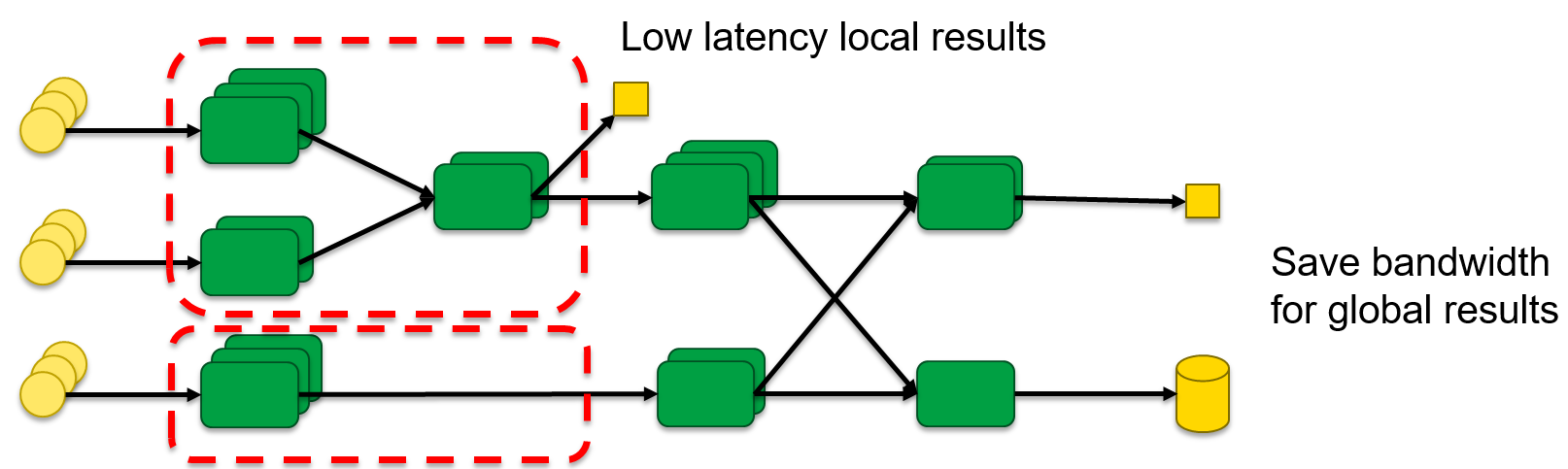
In order to realize our approach, we have implemented a geo-aware scheduler plugin for the Apache Storm stream
processing system. The scheduler takes as an input a Storm topology (Figure 1) to be scheduled and executed on the
available datacenter/edge Cloud resources. The scheduler enables the developers of the topology to annotate groups
of stream processing elements that can be replicated and pushed outside of the data center to an Edge Cloud with
close proximity to the stream source. In order to operate, the scheduler requires knowledge of the available
datacenter/edge Clouds, data stream types available at each Cloud, and latencies among clouds.
Publications
- H. P. Sajjad, K. Danniswara, A. Al-Shishtawy and V. Vlassov, “SpanEdge: Towards Unifying Stream Processing over
Central and Near-the-Edge Data Centers,” 2016 IEEE/ACM Symposium on Edge Computing (SEC), Washington, DC, 2016,
pp. 168-178.




